Later Life Workplace Index
 ©Prof. Dr. Jürgen Deller et al. (2020)
©Prof. Dr. Jürgen Deller et al. (2020)
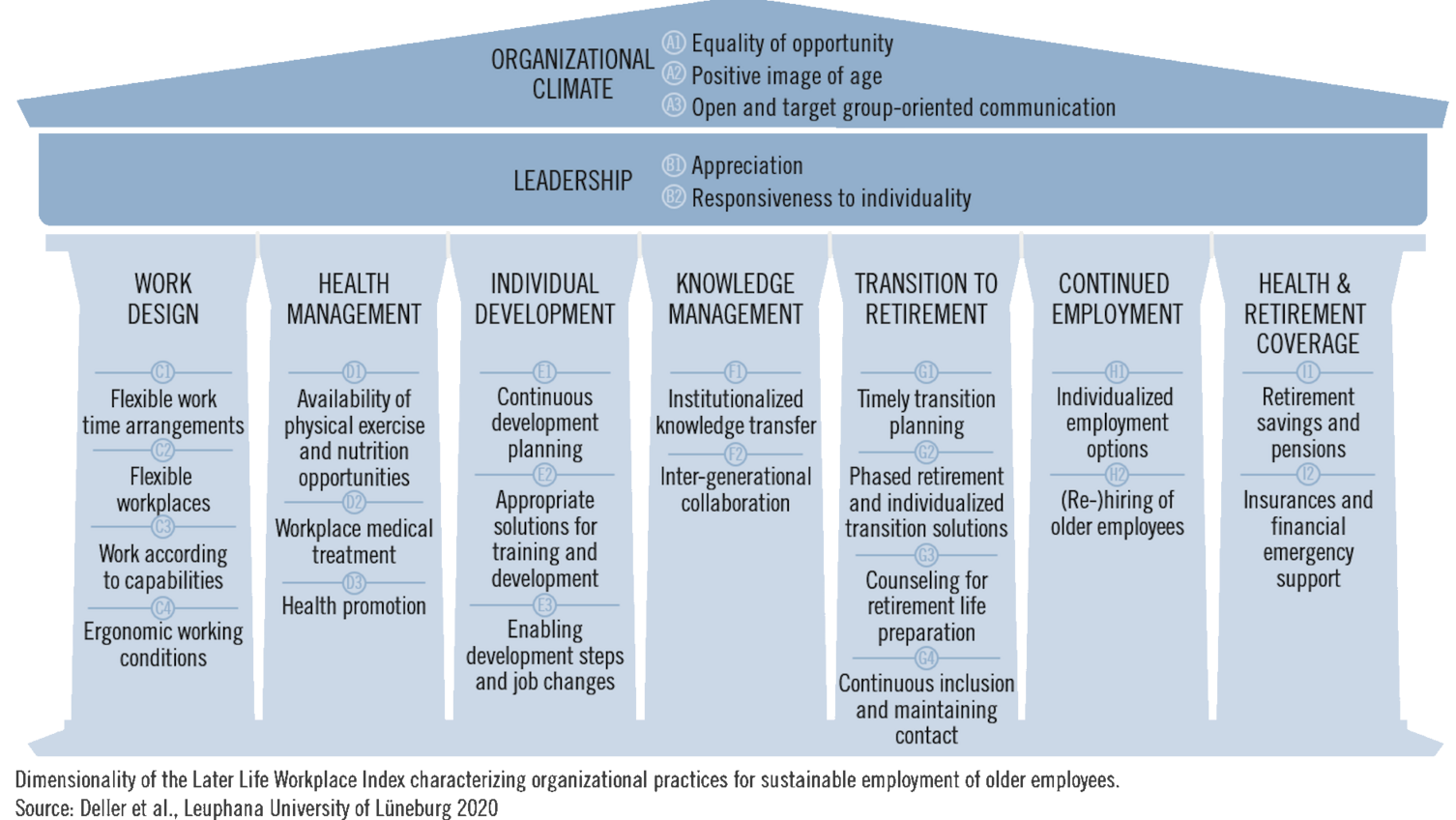
Particularly in times of demographic change and skilled labor shortages, the successful employment of older workers gains importance. But what does an organization look like in which working in older age and working in age-diverse teams is successful? The aim of the Later Life Workplace Index is to answer this question by identifying and measuring organizational practices that maintain and promote the performance, motivation, and health of older workers. The index proposed by Wöhrmann, Deller, and Pundt (2018) provides a systematic framework of existing organizational practices (e.g., in the field of health management, work design, or age-friendly leadership) that can be used by organizations as a self-assessment and benchmark tool. Most of the identified practices do not exclusively benefit older employees but are meaningful for employees of all age groups – they are age-inclusive.
The domains of the Later Life Workplace Index (LLWI) have been developed based on qualitative research in Germany and the U.S. and are displayed in the following figure:
 ©Prof. Dr. Jürgen Deller et al. (2020)
©Prof. Dr. Jürgen Deller et al. (2020)
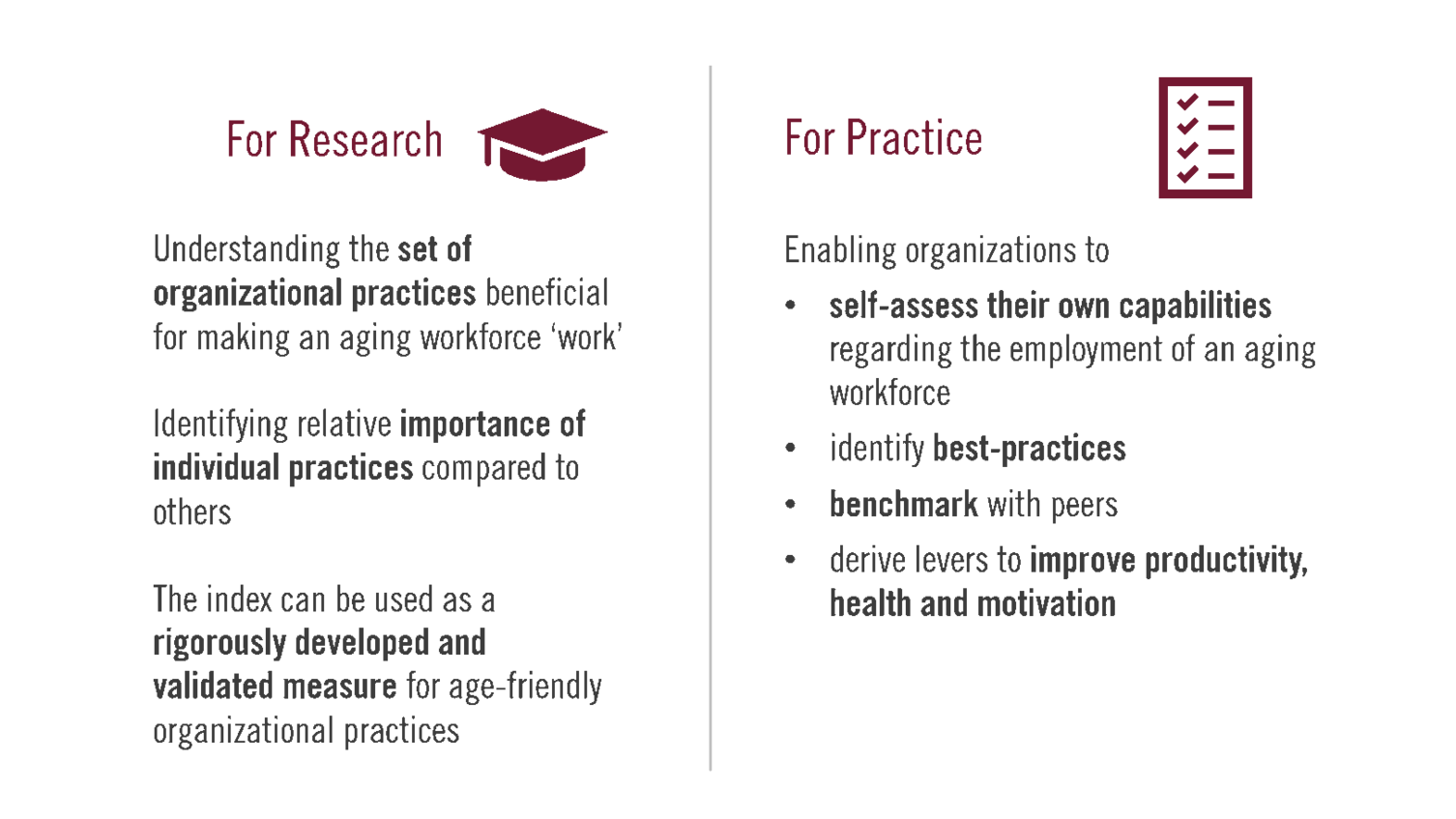
Implications for research and practice
For researchers, the LLWI helps to understand the dimensionality and the relative impact of organizational practices for older workers. The index can be used either as a holistic measurement of organizational practices for older workers or subscales of the index can be used to focus on specific domains to promote research in the field of work and aging.
For practitioners, the LLWI presents an accessible self-assessment tool for organizational practices related to the employment of older workers. By setting benchmarks, organizations can compare their results with other organizations and thus identify their own potential.
 ©Prof. Dr. Jürgen Deller et al. (2020)
©Prof. Dr. Jürgen Deller et al. (2020)
